Levitra Soft
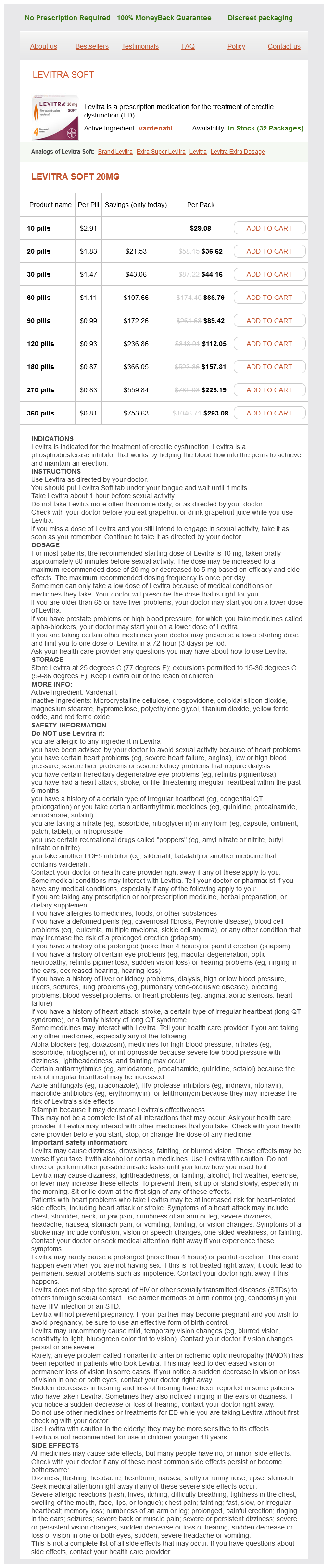
Levitra Soft 20mg
- 10 pills - $29.08
- 20 pills - $36.62
- 30 pills - $44.16
- 60 pills - $66.79
- 90 pills - $89.42
- 120 pills - $112.05
- 180 pills - $157.31
- 270 pills - $225.19
- 360 pills - $293.08
Current recommendations are to postpone surgery for as long as possible erectile dysfunction treatment over the counter buy levitra soft 20 mg on-line, usually beyond the second or third week of the disease or later, when necrotic tissue can be easily distinguished from viable pancreas and debridement without major ´ blood loss can be performed. Necrosectomy can be performed by an open anterior approach with closed lavage or with leaving the abdomen open and packing. This ´ procedure is a combination of percutaneous drainage and the open lateral retroperitoneal approach. An anterior laparoscopic approach has also been described and mimics the open anterior approach using laparoscopic ports. Surgical necrosectomy is indicated in patients with sepsis caused by infected necrosis and in selected patients with extended sterile necrosis causing severe systemic organ dysfunction and sepsis without a septic focus. In some cases, the acute inflammatory process can lead to erosion into retroperitoneal vessels, and acute hemorrhage occurs. Necrotic material debrided from the retroperitoneum in a case ´ of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Monitoring Despite a conservative operative approach, endocrine and exocrine insufficiency develop in as many as half of the patients and are determined by the extent of pancreatic necrosis. Therefore, patients must be monitored with blood glucose measurements, stabilization of body weight, and proper nutrition. Complications the most common complication after successful management of acute pancreatitis is a pseudocyst. In addition, these collections are further classified as sterile or infected and the term ``pancreatic abscess' has been abolished. Most pseudo- cysts resolve spontaneously, even beyond 6 weeks, so asymptomatic pseudocysts are usually observed. Cystjejunostomy (laparoscopic or open) is used in cases in which the site of the pseudocyst precludes drain- age into the posterior aspect of the stomach. A 4 the Digestive System B 162 Chronic Pancreatitis Chronic pancreatitis is a chronic inflammatory disease of the pancreas characterized by irreversible morphologic changes that typically are associated with pain or permanent loss of function, or both. Epidemiology Population studies suggest a prevalence of chronic pancreatitis that ranges from 5 to 27 persons per 100,000 population, with considerable geographic variation. Autopsy data are difficult to interpret because a number of changes associated with chronic pancreatitis, such as fibrosis, duct ectasia, and acinar atrophy, are also present in asymptomatic elderly patients. Differences in diagnostic criteria, regional nutrition, alcohol consumption, and medical access account for variations in the frequency of the diagnosis, but the overall incidence of the disease has risen progressively since the 1960s. Chronic pancreatitis in the United States currently results in more than 120,000 outpatient visits and more than 50,000 hospitalizations per year. Risk factors Alcohol consumption and alcohol abuse are associated with chronic pancreatitis in up to 70% of cases. Other major causes include tropical (nutritional) and idiopathic disease, as well as hereditary causes. There is a linear relationship between exposure to alcohol and the development of chronic pancreatitis. However, chronic pancreatitis can occur in patients who drink very little, and it occurs in less than 15% of documented alcoholics.