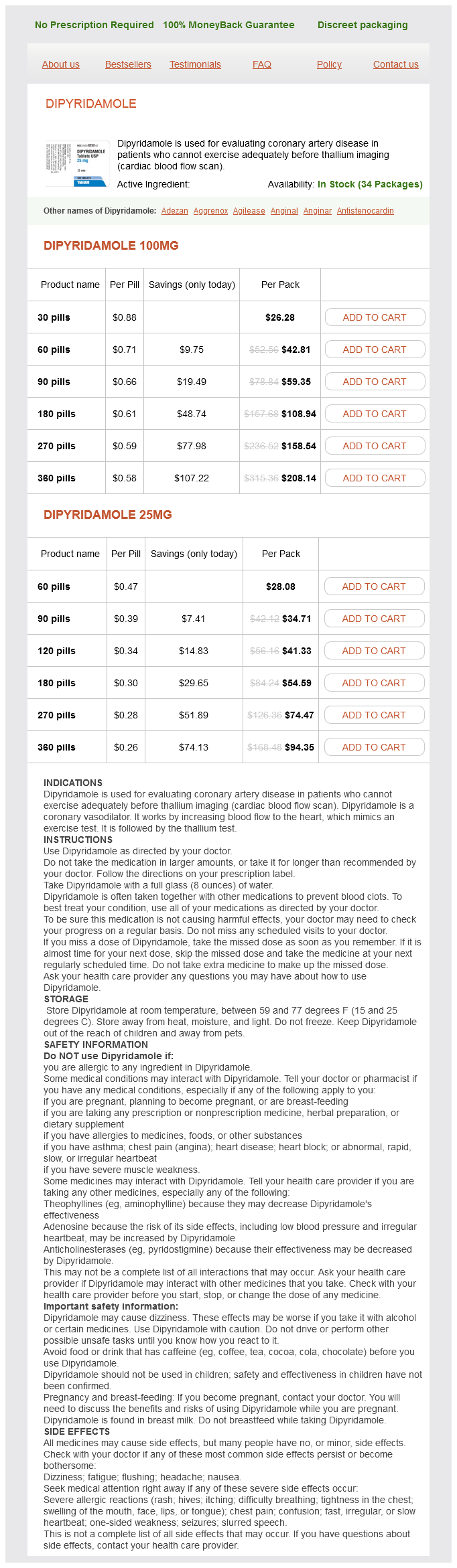
Dipyridamole
Dipyridamole 100mg
- 30 pills - $26.28
- 60 pills - $42.81
- 90 pills - $59.35
- 180 pills - $108.94
- 270 pills - $158.54
- 360 pills - $208.14
Dipyridamole 25mg
- 60 pills - $28.08
- 90 pills - $34.71
- 120 pills - $41.33
- 180 pills - $54.59
- 270 pills - $74.47
- 360 pills - $94.35
Allopurinol is contraindicated in patients who have exhibited serious adverse effects or hypersensitivity reactions to the medication and in nursing mothers and children arrhythmia in 7 year old dipyridamole 25 mg buy mastercard, except those with malignancy or certain inborn errors of purine metabolism. An initial daily dose of 100 mg in patients with estimated glomerular filtration rates greater than 40 mg/ min is increased by 100-mg increments at weekly intervals. Patients with reduced glomerular filtration require a lower dose to achieve the targeted uric acid concentration, and their clinical and pharmacological response needs be monitored frequently. The usual daily dose in children with secondary hyperuricemia associated with malignancies is 150300 mg, depending on age. Allopurinol also is useful in lowering the high plasma concentrations of uric acid in patients with Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (orphan designation) and thereby prevents the complications resulting from hyperuricemia; there is no evidence that it alters the progressive neurological and behavioral abnormalities that are characteristic of the disease. Allopurinol increases the t1/2 of probenecid and enhances its uricosuric effect, while probenecid increases the clearance of oxypurinol, thereby increasing dose requirements of allopurinol. Allopurinol also may interfere with the hepatic inactivation of other drugs, including warfarin. It remains to be established whether the increased incidence of rash in patients receiving concurrent allopurinol and ampicillin should be ascribed to allopurinol or to hyperuricemia. Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in patients with compromised renal function, especially those who are receiving a combination of allopurinol and a thiazide diuretic. The most common adverse effects are hypersensitivity reactions that may manifest after months or years of therapy. Rarely, toxic epidermal necrolysis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome occurs, which can be fatal. The risk for Stevens-Johnson syndrome is limited primarily to the first 2 months of treatment. If indicated, desensitization to allopurinol can be carried out starting at 1025 g/d, with the drug diluted in oral suspension and doubled every 314 days until the desired dose is reached. Oxypurinol has orphan drug status and is available for compassionate use in the U. Fever, malaise, and myalgias also may occur in about 3% of patients, more frequently in those with renal impairment. Therapeutic Use Febuxostat is approved for hyperuric patients with gout attacks but is not recommended for treatment of asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Thus, therapy should be initiated with 40 mg/d and the dose increased if the target serum uric acid concentration is not reached within 2 weeks. An increase in gout flares was frequently observed after initiation of therapy, due to reduction in serum uric acid levels resulting in mobilization of urate from tissue deposits.